Field Related Vocabulary
Electrophysiology technology
I have been in the medical electrophysiology program for over a year now. This glossary is to learn how to pronounce related words to this field of study.
- electrocardiogram
- noun
- a record or display of a person's heartbeat produced by electrocardiography.
- Example: ELECTROCARDIOGRAM monitoring 12 lead ELECTROCARDIOGRAMs (ECG) are used to monitor changes in the electrical activity (PQRST wave) of the heart during thrombolytic therapy to detect coronary reperfusion.
- fr: électrocardiogramme

- Electrodes
- noun
- An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit.
- Example: I will stick some electrodes on your chest, your two hands and your two feet to start the exam.
- fr: Électrodes
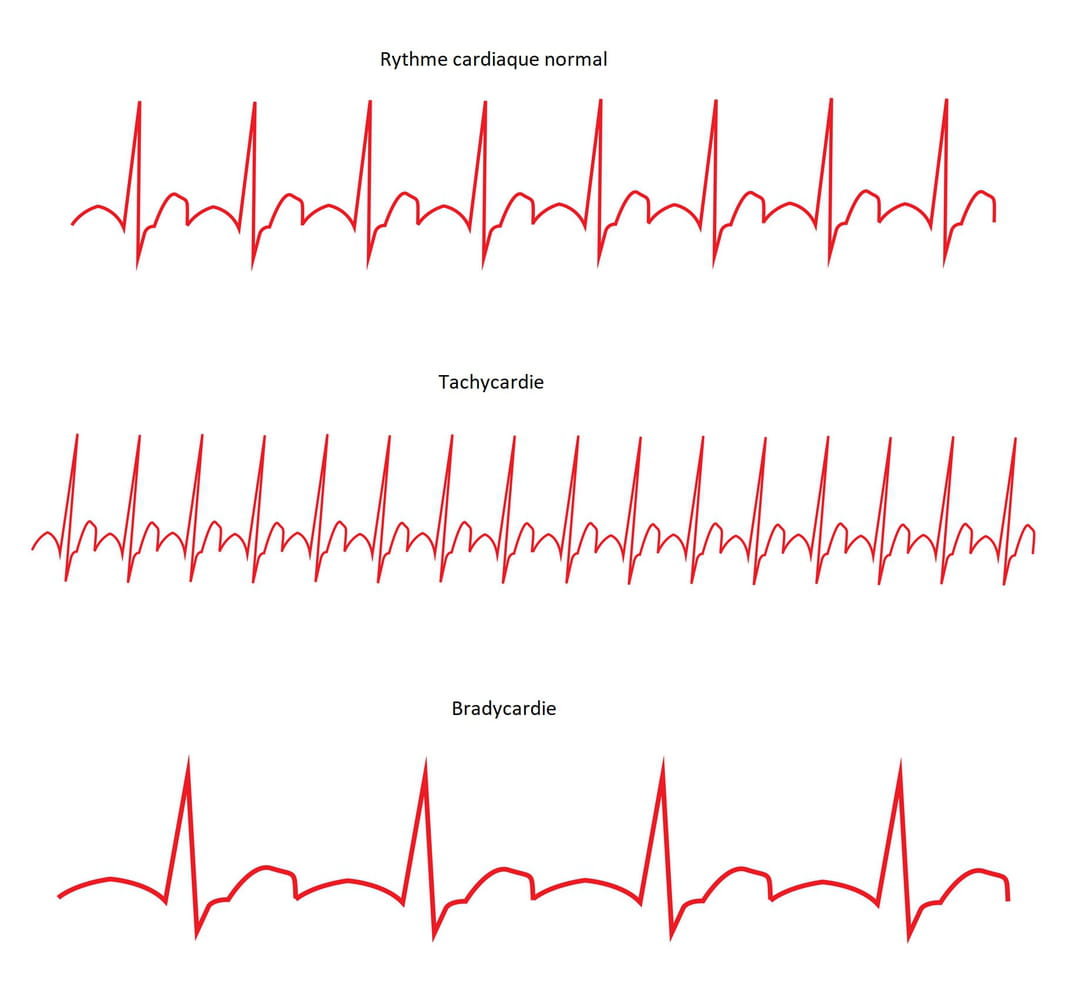
- Bradycardia
- noun
- A heart rate below normal.
- Example: My patient suffers from bradycardia since he was 25 years old.
- fr: Bradycardie

- Tachycardia
- noun
- A heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate.
- Example: My patient is having a tachycardia of 120 bpm.
- fr: Tachycardie

- Electroencephalography
- noun
- is a method to record an electrogram of the electrical activity on the scalp that has been shown to represent the macroscopic activity of the surface layer of the brain underneath.
- Example: My patient is known to have epileptic seizures so the doctor requested to do an electroencephalography exam for him.
- fr: Électroencéphalographie
- Epilepsy
- noun
- A group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures.
- Example: An EEG is an important test for diagnosing epilepsy because it records the electrical activity of the brain.
- fr: Épilepsie

- Neurology
- noun
- A branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system.
- Example: My sister has an appointment in neurology to have an EEG exam.
- fr: Neurologie

- Electromyography
- noun
- A technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles.
- Example: One basic function of an electromyograph is to see how well a muscle can be activated.
- fr: Électromyographie
- Electronystagmography
- noun
- A diagnostic test to record involuntary movements of the eye caused by a condition known as nystagmus.
- Example: The electronystagmography can be used to determine the origin of various eye and ear disorders.
- fr: Électronystagmographie
- Saccade
- noun
- A quick simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of fixation in the same direction.
- Example: Saccades are one of the fastest movements produced by the human body.
- fr: Saccade
- Nystagmus
- noun
- A condition of involuntary eye movement.
- Example: Nystagmus that occurs later in childhood or in adulthood is called acquired nystagmus.
- fr: Nystagmus

- Arrhythmia
- noun
- Is an irregularity in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow.
- Example: Arrhythmias may occur at any age, but are more common among older people.
- fr: Arythmie
- Palpitations
- noun
- Abnormalities of the heartbeat characterized by awareness of cardiac muscle contractions in the chest, which is further characterized by the hard, fast and/or irregular beatings of the heart
- Example: My patient is feeling all his palpitations on his chest and feels pain on his back.
- fr: Palpitations
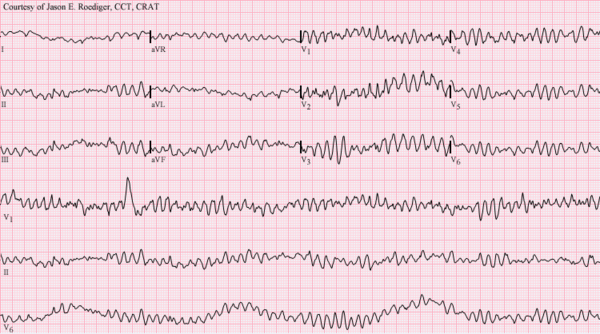
- Ventricular fibrillation
- noun
- An abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver instead of pumping normally.
- Example: Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse.
- fr: Fibrillation ventriculaire
- Ventricle
- noun
- One of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expels blood.
- Example: The right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta.
- fr: Ventricule

- Holter
- noun
- A type of ambulatory electrocardiography device, a portable device for cardiac monitoring for at least 24 to 72 hours
- Example: Each Holter system consists of two basic parts. The hardware for recording the signal, and software for review and analysis of the record.
- fr: Holter
- Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (MAPA)
- noun
- A non-invasive exam that records blood pressure over a period of 24 hours.
- Example: The MAPA can differentiate permanent hypertension.
- fr: Monitoring ambulatoire de pression artérielle (MAPA)

- Cardiomemo
- noun
- A non-invasive way of monitoring your heart's activity. It involves placing a device next to your heart whenever you feel symptoms.
- Example: Wearing a cardiomemo will help allow your doctors to monitor your heart and diagnose any problems.
- fr: Cardiomémo
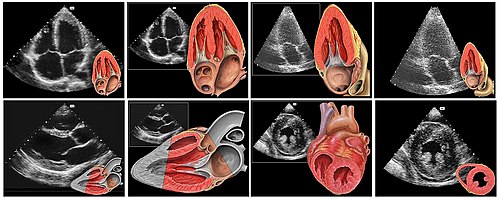
- Echocardiography
- noun
- An ultrasound of the heart.
- Example: The results to my echocardiography was abnormal.
- fr: Échocardiographie
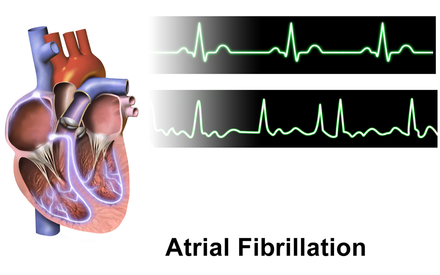
- Atrial fibrillation
- noun
- An abnormal heart rhythm characterized by rapid and irregular beating.
- Example: Atrial fibrillation is usually accompanied by symptoms related to a rapid heart rate.
- fr: Fibrillation auriculaire